Cloud VM (Virtual Machine) – Virtual Partner of your Operating System

The definition of VM is a bit tricky and technical, so let’s start with an example to understand the concept of Virtual Machine.
Suppose you are a Software engineer, and designing software or a mobile application and want to make it responsive to all the environment and want to test its accessibility in all the operating systems like Windows, iOS and Linux. Means you want to check whether your software is working on all the three Operating Systems or not? Similarly, in the case of the mobile app, you want to check whether it is working fine on Android as well as iOS platform or not. What will be your option? Buy different devices with different operating systems and test your software or app on all the devices? Will that be a convenient and affordable option? NO!
Here is where the VM or Virtual Machine comes into the picture. VM allows you to install and operate different Operating Systems on a single computer system without interfering the operation of the original system. It also allows both the Operating Systems to have their virtually separate storage, CPU and Network.
The original system acts as a Host Machine generally referred to as Host; engineers also call it as Host Computer or Host Operating System. The Virtual Machine or Virtual Hardware or an operating system which work inside the Host are called Guest Machine and generally referred to as Guest.
Now the most important part of VM is the software which manages all the operating systems in one single host machine. It is called the Hypervisor. It is a responsibility of Hypervisor to allow a user to switch to the desired operating system, provide an independent environment to all the Guest Machines and protect the Host as well.
Hypervisor – Types and Functions
There are 2 types of Hypervisors
1. Hypervisor Type 1
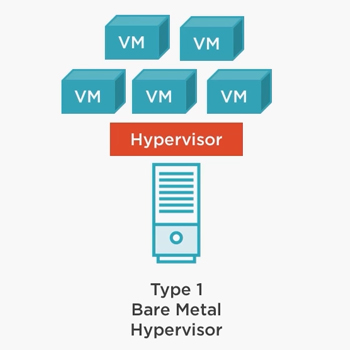 The Hypervisor Type – 1, interacts directly with the host Hardware and installed on “Bare Metal”. That is why in technical terms it is also referred to as Bare-Metal Hypervisor. It is not dependent on another Operating System as it runs directly on physical hardware, for example, if your system is Intel operated or AMD operated, and you have Type – 1 Hypervisor than the Intel or AMD will take care of all the operating systems and no other Operating Systems interference is required.
The Hypervisor Type – 1, interacts directly with the host Hardware and installed on “Bare Metal”. That is why in technical terms it is also referred to as Bare-Metal Hypervisor. It is not dependent on another Operating System as it runs directly on physical hardware, for example, if your system is Intel operated or AMD operated, and you have Type – 1 Hypervisor than the Intel or AMD will take care of all the operating systems and no other Operating Systems interference is required.
Now, in a simple word the Type – 1 Hypervisor is placed between Hardware and the Operating System, and hardware becomes the Host while all the Operating systems work as Guests. No operating system is dependent on Host OS they all are dependent and operated by Hardware.
You will get more idea once you understand the operation or process of Type – 2 Hypervisor.
Examples of Hypervisor – 1, are Citrix/Xen Server, VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
2. Hypervisor Type 2
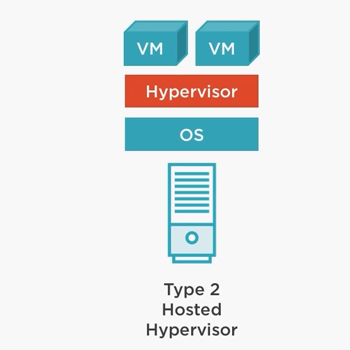 The second type of Hypervisor is completely dependent on the Host Operating System or Pre-existed operating system. This Hypervisor is installed on the Host Operating System and the Host OS Manages and Operates the machine and handles the CPU, Network and Memory/Storage for the Virtual Machine or a Guest Machine.
The second type of Hypervisor is completely dependent on the Host Operating System or Pre-existed operating system. This Hypervisor is installed on the Host Operating System and the Host OS Manages and Operates the machine and handles the CPU, Network and Memory/Storage for the Virtual Machine or a Guest Machine.
In Simple word Type – 2 Hypervisors are placed after or on top of Operating System of Host Machine. There will be an application or software installed on the Host Operating System which will lead the user to the Guest VMs and switching between multiple VMs or Managing their performance. The communication of the Guest VM to CPU, Storage and Hardware is also managed by the Host OS
Examples of Hypervisor – 2 are Microsoft Virtual PC, Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, Oracle Solaris Zones, VMware Fusion, Oracle VM Server for x86 and more.
Working & Operation of VMs
Virtualization allows you to share a system with many virtual machines, means you can operate multiple machines from one single machine.
The Hypervisor assists and communicates with Hardware or the Operating System (based on the type of Hypervisor) to fulfil the requirements of VM from the resources of the system whether it is related to processing, computing, memory allocation or storage.
Benefits of VMs
Multiple Operating Systems at one Computer
 User can access multiple operating systems and hence the user can choose the OS as per their preference, for example, you are using Apple System but you want to use MS Word or any other feature of windows 10, you may switch to VM through VirtualBox Windows 10; work as per your convenience and come back to iOS.
User can access multiple operating systems and hence the user can choose the OS as per their preference, for example, you are using Apple System but you want to use MS Word or any other feature of windows 10, you may switch to VM through VirtualBox Windows 10; work as per your convenience and come back to iOS.
Data Security
 When a user creates a virtual machine, creates a virtual hard disk. Hence, the crash or virus attack on VM will not affect the data on Host Hard Disk. User can also use the Cloud Virtual Machine to protect the data and save the space on a hard disk.
When a user creates a virtual machine, creates a virtual hard disk. Hence, the crash or virus attack on VM will not affect the data on Host Hard Disk. User can also use the Cloud Virtual Machine to protect the data and save the space on a hard disk.
Pocket Friendly
As we understood that user need not buy the physical inventory to operate different operating environment; the cost of Hard Disk, Processor, Monitor and another common component can be avoided. The user can operate all the desired Operating Systems using the same physical equipment.
Testing is made easy
Testing of newly built app and software is made easy through virtualbox whether it is virtualbox 64 bit or virtualbox 32 bit. If you are a software developer or a web designer or an app creator, you don’t have to rely on other users to give feedback on your product for different operating systems. You can test all your products on your system using all the available Operating Environment and be sure of your product before launching it. This will reduce the gap between testing and launching phase, as you can test it, make required amendments and fix the bugs at once all by yourself.
The VM is a “must-have” technology for all the aspiring and successful engineers!
We, at PremWare, are always happy to help you for any information or services for Virtual Machines near you, VM is just a call away for you…Contact us for Virtual Machine anywhere in Surat, Gujarat.
Interested in cloud? You might be interested in our below cloud related blogs:
Why Switch to the Cloud? – 11 Advantages of Cloud Computing for Business
Why to choose Azure Cloud: 10 Reasons Why to choose Microsoft Azure Cloud for Your Enterprise
Cloud Servers vs Physical Servers: Definition, Features, Pros and Cons of Cloud and Physical Server
Azure Vs AWS: Why choose Azure over AWS?
What is a Virtual Machine (VM)? – The Benefits of Virtual Machines
Cloud vs Virtualization: What’s the difference between Cloud Computing and Virtualization?
1win
1вин
